What is ERP and How It Works: ERP Systems Explained
What is an ERP system, how does it work, and why should you invest in it? Here, we explain what ERP stands for and reveal why the solution benefits your business.
Whats Is ERP in Brief

ERP systems offer visibility into your entire business operation by monitoring all stages of production, logistics, and finances. These cohesive systems function as the central nexus for a business's complete workflow and data, enabling various departments to access crucial information.
History of ERP Systems
The first generation of ERP systems was based on mainframe computers and was introduced in the 1960s. These early systems were designed to handle inventory control and order processing but lacked flexibility and scalability. Moreover, since they were so expensive, only large companies with significant resources invested in them.
The second generation of ERP systems emerged in the 1980s and early 1990s and was built on minicomputers and workstations. These systems could support multiple users and applications, but they were still expensive and not accessible to smaller companies.
The third (and the latest) generation of ERP systems uses cloud technology, which allows multiple users to access information stored on a server over a network connection. This makes it possible for businesses of all sizes to own an ERP system without investing thousands of dollars in infrastructure.
How Does a Modern ERP System Work?
Switching to the cloud, especially with the software-as-a-service (SaaS) model for ERP, means that ERP software is hosted on remote servers rather than on-site. The cloud provider handles software updates regularly, saving companies from costly upgrades every 5 to 10 years. This shift reduces both operational and capital expenses because companies no longer need to buy software or hardware or hire extra IT staff. Instead, they can invest these resources in new business ventures.
Plus, staying on the cloud ensures that the organization always has access to the latest ERP software. With IT management taken care of, employees can focus on more productive tasks like innovation and expansion.
Business Value of ERP
As you enter critical business data into an ERP system, you can align different departments across locations to streamline your business workflows, leading to significant savings.
Here are the key values that an ERP system brings to your business:

Types of ERP
ERP Features
Finance & Accounting
Supply Chain & Procurement
Key features include:
Project Management

HR & Payroll
Key features of the HR and payroll module include:
Get Started With FirstBit ERP System
Project costs analysis. Control your project costs and avoid cost overruns.
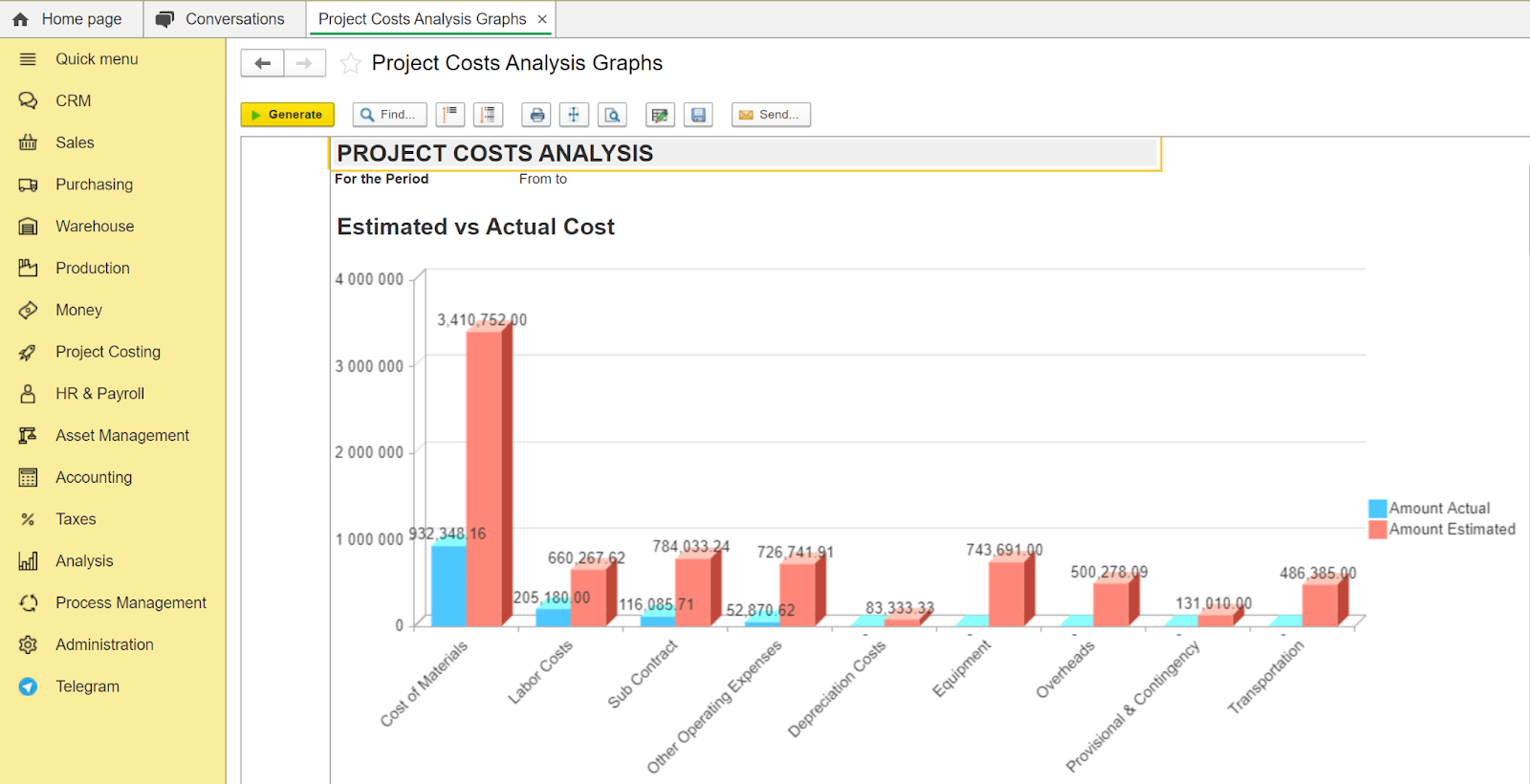
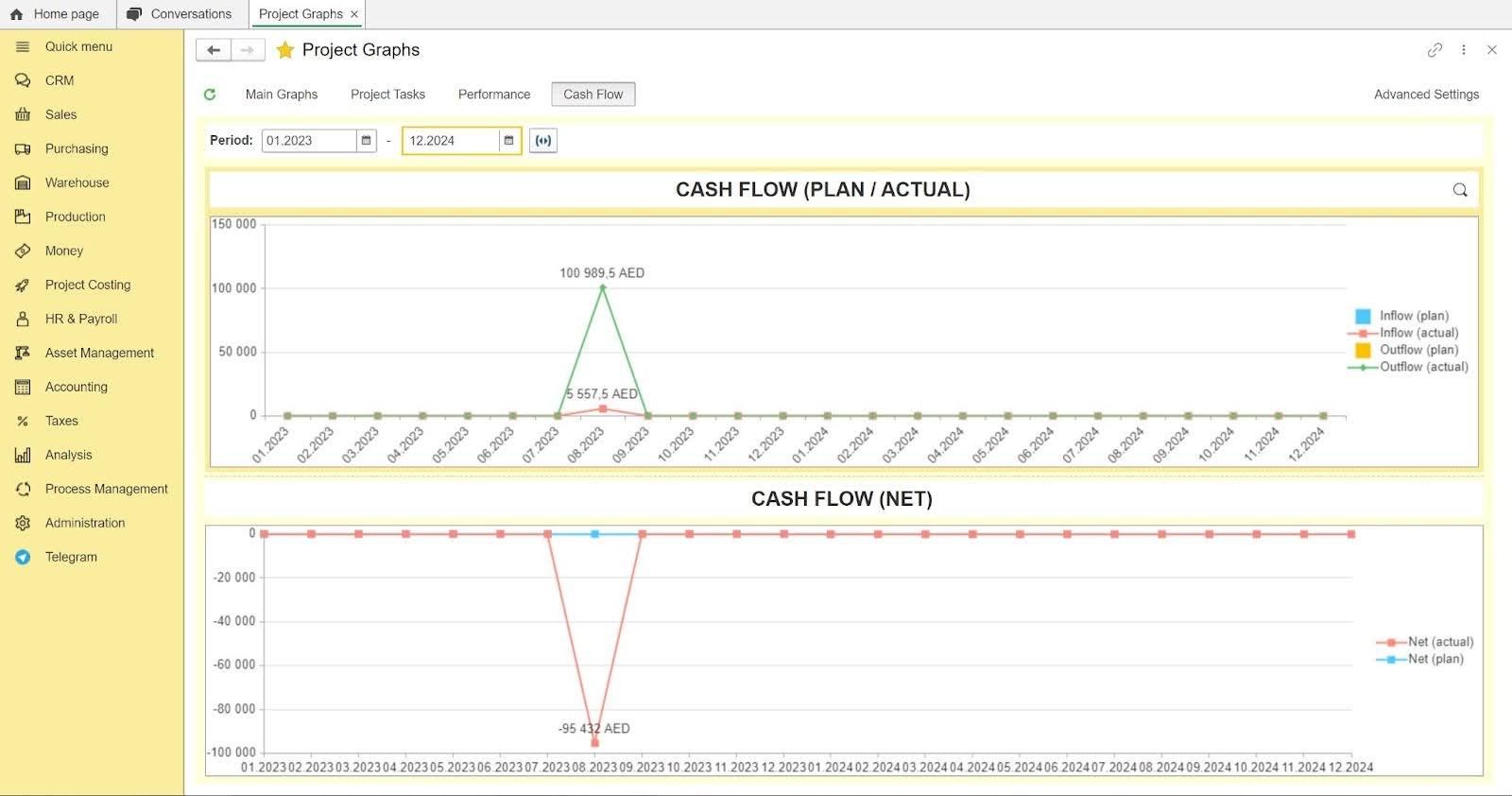
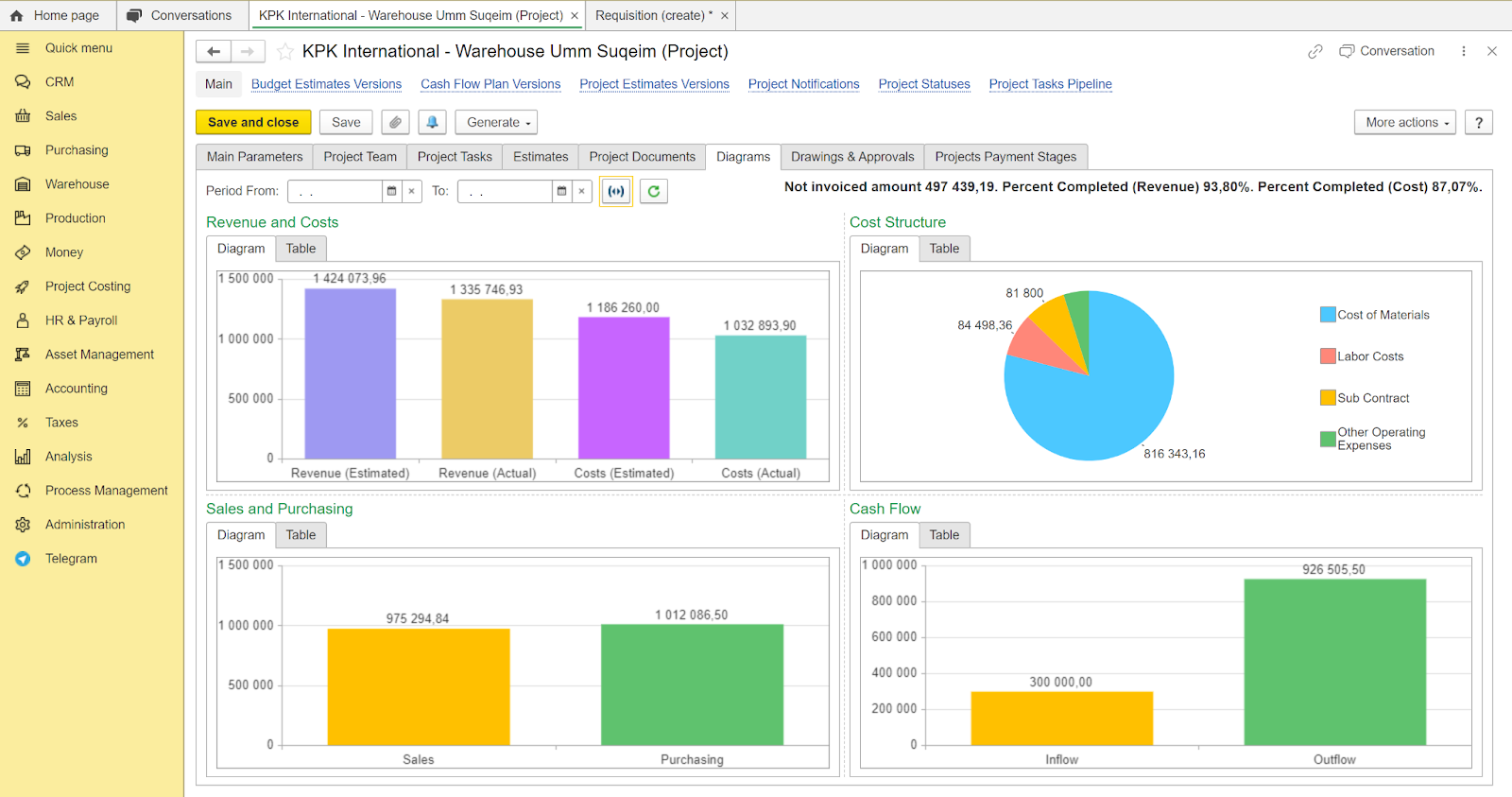
One of the biggest benefits of the FirstBit ERP system is that it is FTA-accredited software. It also ensures full compliance with IFRS. This means that you won’t have to worry about financial or tax compliance in the UAE.
Also, you can integrate the FirstBit ERP system with front-office applications like CRM to build a holistic view of your business operations.
FAQ
What’s the Difference Between ERP and Financials?
Financials, on the other hand, is a finance management tool that helps you track your company’s performance over time (in terms of revenue). It includes the numbers behind your business’s financial performance. These include income statements (profit & loss statements) and balance sheets (assets, liabilities & equity).
Financial software usually includes compliance with the necessary reporting requirements, such as the International Financial Reporting Standards Foundation (IFRS), Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), and local laws.
While financials focus on one area of the business, ERP software comprises a wide range of business processes (which includes financials).
What's the Difference Between ERP and Accounting Software?
On the other hand, ERP software offers a comprehensive solution that integrates various business processes beyond finance, including supply chain management, human resources, customer relationship management, project management, inventory tracking, warehouse management, eCommerce, and more.
What’s the Difference Between ERP and Financials?
How Does ERP Help Companies to Grow?
of your processes and scale your business with FirstBit ERP now!









