Phases of an ERP Implementation Plan
This article will guide you through the key phases of ERP implementation. As you read, note how each step applies to your unique projects and challenges. By the end, you'll have a roadmap to successfully implement an ERP system that streamlines your operations and addresses your specific management hurdles.
Key Phases For a Seamless ERP Implementation
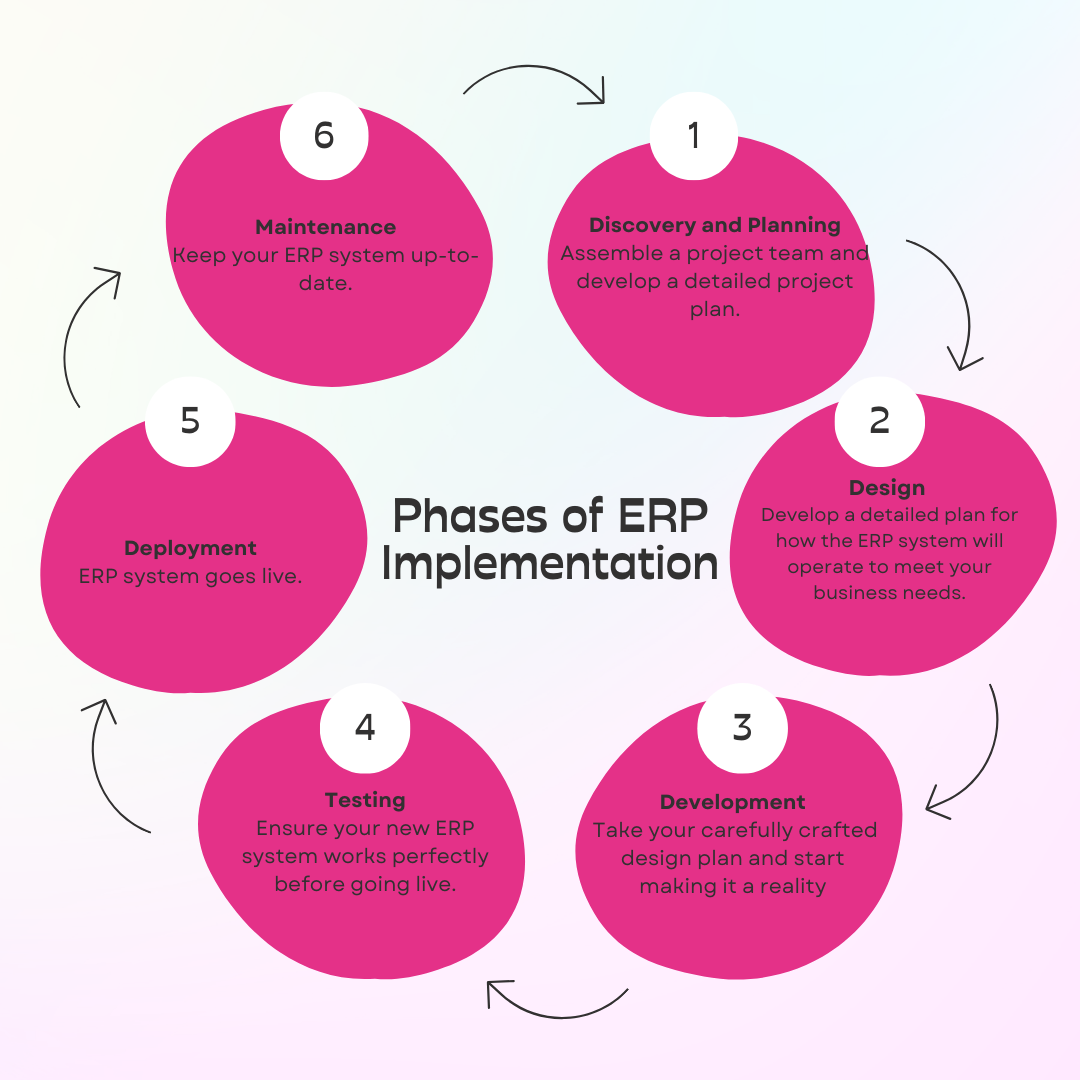
1. Discovery and Planning
During this phase, you'll assemble a project team and develop a detailed project plan. This team will be responsible for setting deadlines, allocating resources, making ERP system decisions, and managing daily tasks. A diverse team can help in identifying and addressing issues throughout the project.
Begin by thoroughly reviewing your current business processes. This involves examining how your systems and workflows operate across various departments to identify potential challenges and risks. Key areas to assess include:
2. Budgeting

3. Designing Your ERP System

4. Development
If the standard ERP features don’t fully align with those needs, the vendor will collaborate with the business to customize the system. This could involve adding new features or modifying existing ones to fill any gaps.
While the vendor is customizing the system, they will also prepare training materials to help the business’s team get comfortable with the new ERP. These materials should be clear and relevant to the specific tasks the users will be performing, ensuring a smoother transition to the new system.

5. Testing

Need support to make your ERP transition seamless?
6. Deployment
Ensure Project Team Readiness
Plan for a Smooth Go-Live
Monitor Post-Implementation
7. Maintenance
Guide to Planning Your ERP Implementation
1. Define Your Business Needs
2. Evaluate All Available ERP Solutions
3. Form a Dedicated Implementation Team

4. Develop an ERP Implementation Plan
Together, define the project scope by clearly outlining what the ERP solution will include and exclude. Both parties should agree on the criteria for measuring success, such as timelines and costs.
Next, work together to outline the ERP system's functions, how it will be implemented, and any interim activities required before full deployment. Additionally, create a joint risk assessment plan to anticipate and address potential challenges.
5. Describe All Your Business Processes To Combine Them
For example, marketing and sales teams both need data, so integrating their tools with the ERP will provide a unified source of information, enhancing personalized offerings.
6. Provide Employee Training
7. Ensure User Buy-In
8. Identify Possible Improvements
By following these steps, you'll ensure a smooth ERP implementation process that meets your business needs and drives overall success.
ERP Implementation Best Practices
Choosing the Right ERP System
For a smooth transition with minimal disruption, consider FirstBit ERP. Our customized solutions offer:
FAQs
Q: Which is the Most Critical Phase in ERP Implementation?
Q: Which Phase is the Most Difficult in ERP Implementation?
Q: Why is careful data migration important?
Q: When is the best time to implement ERP software?
Q: How much does an ERP Implementation cost?
of your processes and scale your business with FirstBit ERP now!











