The United Arab Emirates has built its reputation on delivering projects that reshape cities and set new global benchmarks in design, infrastructure, and scale. In 2026, this momentum continues with a series of megaprojects that highlight the country’s ambition to expand capacity, diversify the economy, and invest in long-term sustainability.
For those working in construction and related industries, these developments are not just milestones on a skyline. They influence material prices, drive demand for skilled labor, and affect project timelines across the market. Staying informed about what is underway helps businesses anticipate cost pressures, adjust planning, and remain competitive in a fast-moving sector.
This article explores five of the most significant projects under development in 2026, each representing a different aspect of the UAE’s future urban and economic landscape.
Top 5 Construction Mega-Projects Shaping the UAE in 2026
Here are five of the most significant projects shaping the UAE’s construction landscape in 2026, each illustrating the scale of investment and ambition driving the sector forward.
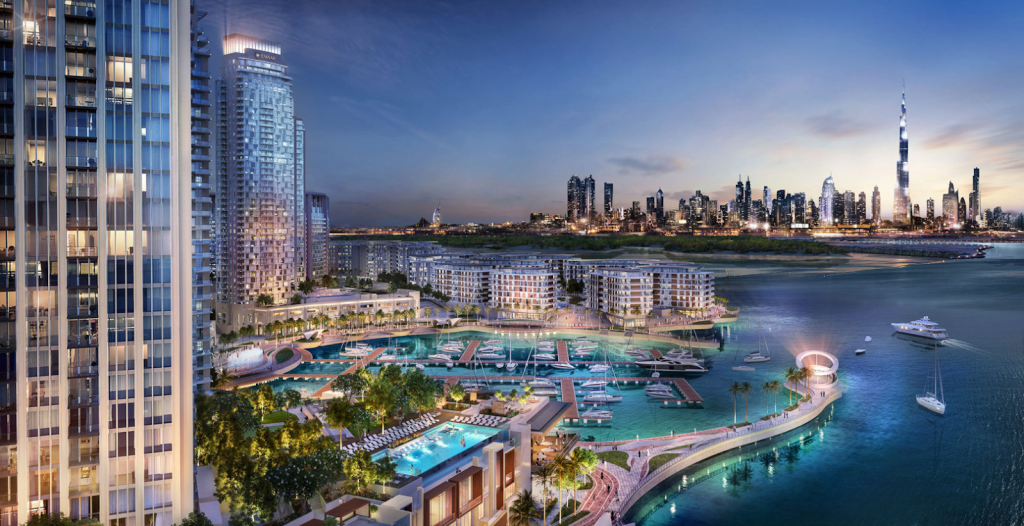
1. Dubai Creek Tower and Dubai Creek Harbour
Dubai Creek Harbour is one of Emaar’s flagship master-planned communities, spanning 1,480 acres along Dubai Creek and designed to integrate residential, retail, cultural, and leisure spaces with views of the Ras Al Khor Wildlife Sanctuary.
At its core is the highly anticipated Dubai Creek Tower, designed by Santiago Calatrava as the architectural centerpiece of the development.
Overview and features:
-
The tower’s design draws inspiration from the form of a lily flower and traditional minarets, combining a sleek spire with a cable-supported structure.
-
It will host multiple observation decks, including a panoramic Pinnacle Room, offering sweeping views of the city and beyond.
-
Creek Harbour itself is envisioned as a mixed-use waterfront district with smart infrastructure, green spaces, and vibrant cultural venues.
Timeline and Current Status
Work on the tower began with foundation works before construction was paused in 2020. In 2024, development was restarted with a revised design. When completed, it is expected to become one of Dubai’s most iconic landmarks.
In early 2026, Emaar Properties confirmed that the construction tender for the redesigned Dubai Creek Tower will be issued within the next three months, marking the formal restart of the project
[?]
. The new vision shifts focus from breaking height records to emphasizing architectural quality and experience, as the tower becomes a symbol of Dubai Creek Harbour.
The tower’s originally proposed extreme height, which would have surpassed the Burj Khalifa, has been scaled back; however, it is still expected to be one of the world’s tallest structures once completed.
With tenders launching in Q1 2026 and foundation work already completed, the tower is expected to progress more rapidly once a main contractor is appointed. An estimated completion date around 2029–2030 is frequently cited, although the final timeline remains flexible.
Dubai Creek Harbour supports the emirate’s ambition to expand livable communities while diversifying tourism and real estate offerings. The tower itself is planned to reinforce Dubai’s global brand as home to record-breaking architecture and serve as a focal point for the city’s eastward expansion.
2. Dubai Cycle City – Part of the 2040 Master Plan
Dubai Cycle City is part of the emirate’s 2040 Urban Master Plan, aiming to position Dubai as one of the most bike-friendly cities in the world. Developed by URB, the initiative aligns with the “20-Minute City” concept, where residents can access most daily needs within a short cycling or walking distance.
Overview and features:
-
The centerpiece is The Loop, a 93-kilometer climate-controlled cycling and running highway powered by renewable energy.
-
The system is designed with vertical farms, shaded public spaces, and smart irrigation using recycled water.
-
Integrated facilities will provide hubs for recreation, fitness, and community activities along the cycling corridor.
Timeline and Current Status
The master plan was unveiled in 2023, with pilot sections of The Loop under early development. Full build-out will be phased toward 2040, aligned with broader city planning initiatives and population growth forecasts.
Cycle City supports Dubai’s goals for sustainable mobility, public health, and livability. Encouraging active transport reduces car dependency and emissions while promoting wellness. It also enhances Dubai’s global brand as a forward-looking city investing in resilient, people-centered infrastructure.
3. Etihad Rail Network
The Etihad Rail Network is the UAE’s flagship national railway system, designed to link all seven emirates and integrate with wider Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) rail plans.
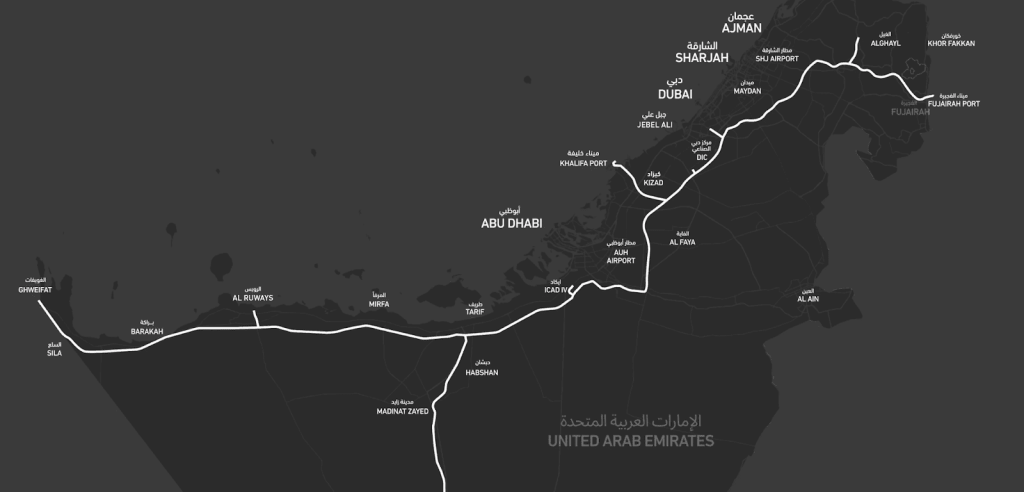
Stretching nearly 1,200 kilometers from Ghuwaifat on the Saudi border to Fujairah on the east coast, the network is being developed in phases to handle both freight and passenger transport.
Overview and features:
-
Stage One, already in operation since 2016, spans 264 km and carries granulated sulfur from Shah and Habshan gas fields to Ruwais port.
-
The full network will connect major ports and industrial zones, including Jebel Ali, Khalifa Port, and Fujairah Port.
-
Future passenger services will run at speeds of up to 350 km/h, linking Abu Dhabi, Dubai, and Fujairah in as little as 50 minutes.
-
Integration with urban systems is also planned, with unified ticketing across metro, bus, and taxi networks.
Timeline and Current Status
Since 2023, freight operations have expanded nationwide, and the system has already moved millions of tons of cargo. Passenger services are under development, and the first trains are expected to launch in 2026. In 2024, Oman Rail and Etihad Rail launched the 303-km Hafeet Rail link between Abu Dhabi and Sohar, marking the UAE’s first international rail connection.
Etihad Rail is preparing to launch passenger train operations in phases throughout 2026
[?] , marking the first time residents and visitors will experience a national rail network in the UAE. Passenger stations will be located in the key centers such as Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Fujairah, Sila, Al Dhannah, Mirfa, Madinat Zayed, Mezaira’a, Al Faya, and Al Dhaid
[?] .
As of now, by shifting large volumes of goods to rail, Etihad Rail has already reduced dependence on road freight and cut carbon emissions by up to 80% compared to trucks. This shift also enhances safety, reduces congestion, and establishes the UAE as a logistics hub linking the Gulf to global trade routes.
Regarding passenger services, the network promises fast and affordable intercity travel, complementing air and road transportation systems.
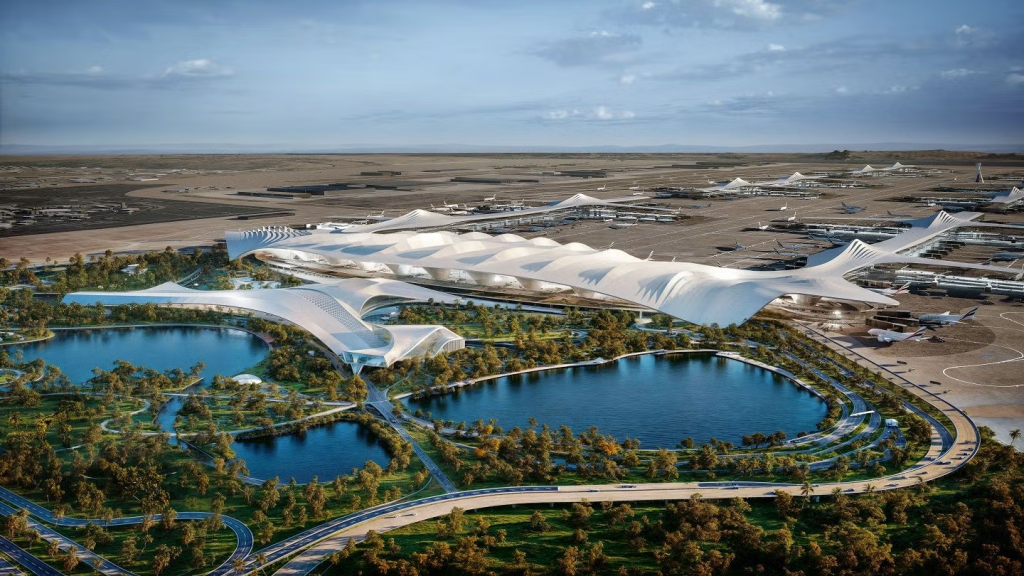
4. Al Maktoum International Airport Expansion
Spread across 70 square kilometers and designed with more than 400 aircraft gates, the project integrates automated travel systems, AI-powered security, and robotic staff to create a new benchmark in aviation.
Timeline and Development
The airport will open in phases, with first operations expected in 2032, according to Khalifa Al Zaffin, Executive Chairman of Dubai Aviation City Corporation.
[?]
Contractors have been mobilized, and an AED 1 billion contract has already been awarded for a second runway.
Phase One Capacity
When the first phase is complete, the airport will be equipped to handle 150 million passengers annually. Key components include:
Dubai International Airport (DXB) remains the busiest international hub, serving 86.9 million passengers in 2023. However, its urban location limits future growth. The expansion of Al Maktoum International will:
-
Unlock capacity to support Dubai’s growing tourism, which reached 17.15 million international arrivals in 2023.
-
Enable Dubai to meet its D33 economic agenda, which targets AED 100 billion in new tourism investments.
Once operational, Al Maktoum International will give Dubai the scale and flexibility it needs to remain the world’s leading aviation hub well into the future.
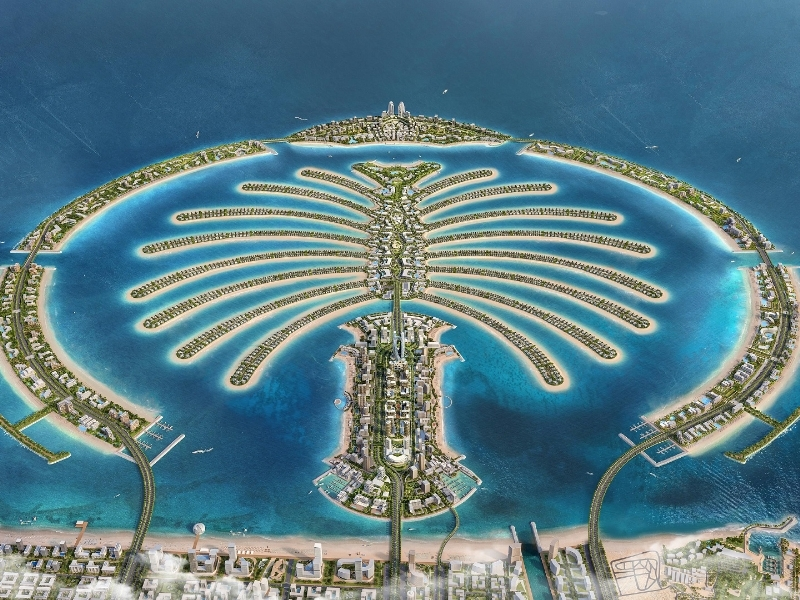
5. Palm Jebel Ali Redevelopment
Palm Jebel Ali is Nakheel’s reinstated mega-island project. It’s an expansive redevelopment of the artificial archipelago off Dubai’s Jebel Ali coast. Originally launched in 2002 and paused in 2008, the project was formally relaunched in 2023 and is now one of the largest urban enhancements underway in the UAE.
Overview and features
Intended to be 50% larger than Palm Jumeirah, the redevelopment will include 16 fronds, over 90 kilometers of beachfront, six marinas, residential zones, waterfront villas, a yacht club, eco-resorts, and mixed-use leisure districts.
Future infrastructure plans call for smart connectivity, pedestrian-friendly neighborhoods, and partial reliance on renewable energy to support sustainability goals.
Timeline and Current Status
Palm Jebel Ali is a mix of ultra-luxury residences and integrated amenities designed to capture global investment, while enabling urban expansion beyond the city’s current limits. The project was relaunched by master developer Nakheel with construction restarting in recent years following a long hiatus that began after the financial crisis
[?]
.
Phased delivery timelines are becoming clearer, although full project completion remains a long-term goal. Early residential units, particularly on certain fronds, are progressing, with handovers targeted for late 2027 to 2028 for the initial homes. However, other parts of the development are still in the early stages of construction, with later delivery dates extending toward 2029 and beyond.
Infrastructure projects will remain a key focus through 2026
[?]
. Nakheel has awarded significant contracts — collectively worth hundreds of millions of dirhams — to advance critical road, utility, and marine infrastructure. It is expected that much of the base infrastructure will be completed by the fourth quarter of 2026, enabling further phases of construction and community activation.
Key Challenges in Mega-Project Management
Like most large-scale construction projects, these projects face recurring hurdles that can quietly undermine schedules and add pressure to delivery.
Budget Overruns and Cost Control
Global data shows that over 11% of megaprojects are at high risk of major delays or cancellation, often due to escalated costs and changing scopes.
For projects like Creek Tower,
initially valued at AED 3.67 billion but paused mid-construction, redesigns and developer-led reinvestment (like the proposed $3.8 billion revival) highlight how indefinite suspensions inherently risk financial instability.
Procurement Delays and Supply Chain Risk
While specific incidents are scarce in public reporting, insider coverage and architectural forums remark on the unusual logjams for Dubai Creek Tower — after 2018 foundation works, tenders stalled and no building contracts were awarded until much later, delaying timelines sharply. That kind of procurement slowdown dramatically increases cost risk.
Workforce Productivity and Subcontractor Tracking
The UAE construction
relies on a multi-national workforce, with staff from different cultural and religious backgrounds. With a diverse, multinational workforce, religious and cultural observances across groups influence work scheduling and require careful planning.
The industry also faces
a shortage of skilled labor and professionals. Demand for engineers, technicians, and experienced site workers is high, but turnover is frequent. During peak construction periods, these shortages can significantly slow delivery.
Another challenge stems from the climate. Summer heat in the Gulf significantly impacts worker productivity and safety, requiring strict scheduling adjustments and cooling measures. Productivity often slows during these months, and projects risk falling behind schedule if this isn’t considered. To stay on track, timelines must be created by experienced planners who can account for weather conditions rather than relying on optimistic assumptions.
Regulatory compliance and documentation
Projects of such a high scale face layers of regulatory approvals that must be updated as designs evolve.
The Creek Tower redesign, for instance, required renewed reviews and documentation, prolonging the restart process. Each new iteration of a project brings added paperwork, inspections, and approval cycles, which can extend timelines even when financing is secured.
For foreign contractors, the requirement to partner with local firms — often with a mandated 51% local stake — further complicates decision-making, particularly if disagreements arise. [?]
In practice, this means the local partner holds majority voting power in the joint venture, even if the foreign contractor brings the technical expertise and capital. When disagreements arise over budgets, timelines, or subcontractor selection, the local partner’s approval is legally decisive. This can slow down procurement, design revisions, or even dispute resolution, as every major change requires alignment between parties who may have different priorities.
Spot emerging trends and adapt fast
Monitor cash flows, project P&L, and KPIs
Request a demo
Top FirstBit ERP Features for the UAE Construction Industry
Managing construction in the UAE means dealing with complex projects, strict labor regulations, and fast-changing market conditions. FirstBit ERP is designed to address these challenges by uniting financials, HR, procurement, and project controls in one system.
Key ERP Features for Mega-Project Execution
For companies handling mega-projects, this integration reduces manual work, minimizes compliance risks, and ensures management always has real-time visibility into costs, schedules, and workforce activity.
The system combines several functions that directly support large-scale construction:
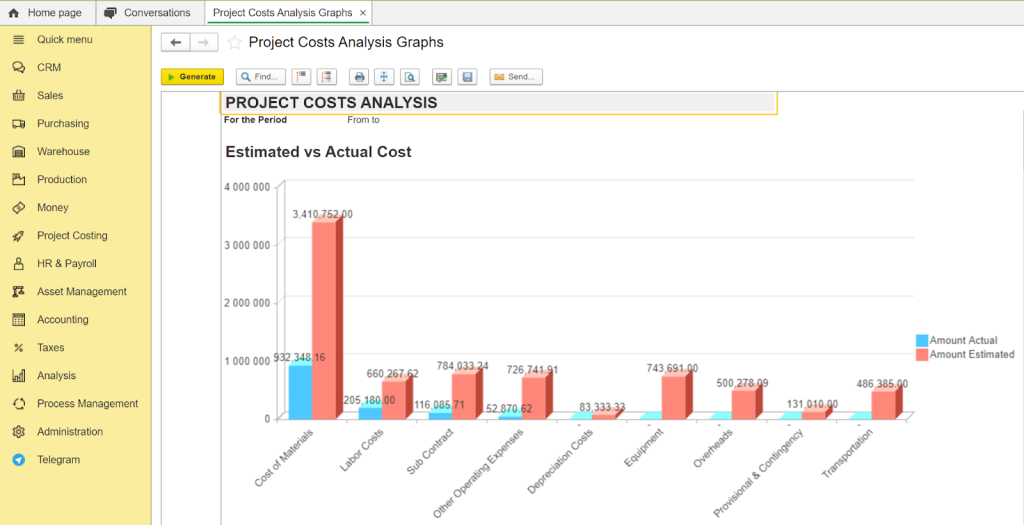
Project costs analysis in FirstBit ERP
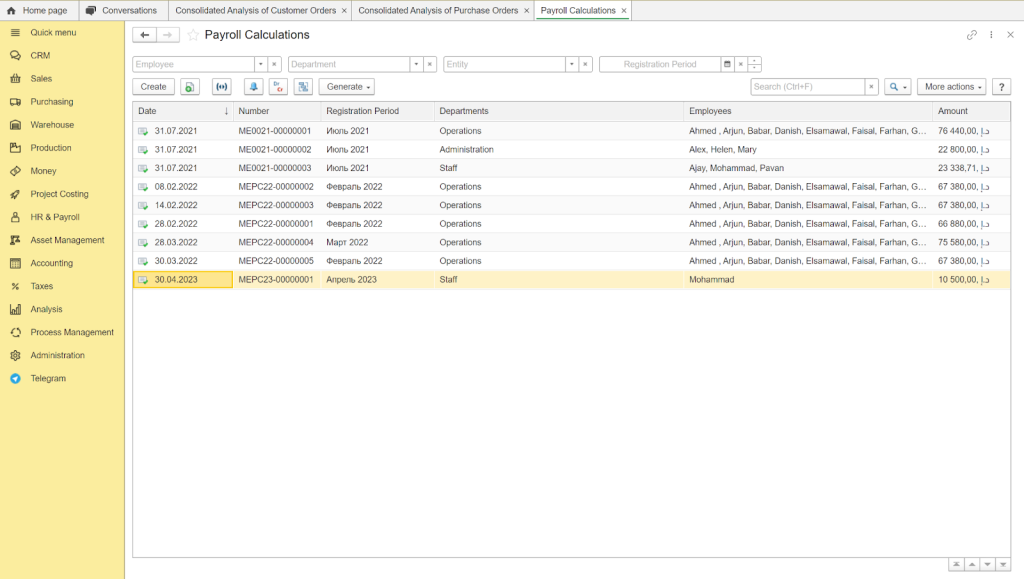
Payroll calculations list in FirstBit ERP
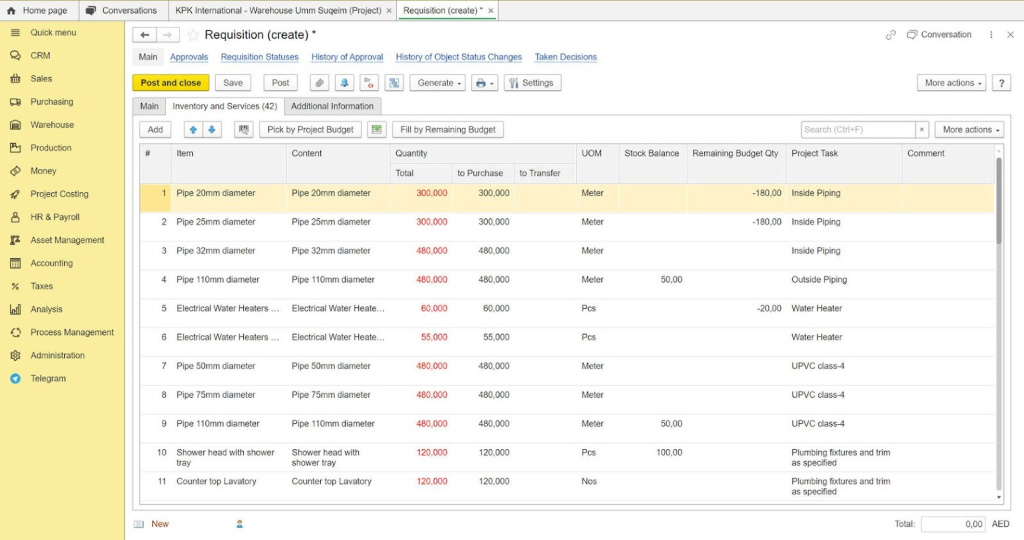
Requisition in FirstBit ERP
VAT on retention amounts in FirstBit ERP
Real-world use case: Kamal Khawaja Building Contracting LLC
Kamal Khawaja Building Contracting LLC
needed a way to reduce the heavy manual workload in HR and improve accuracy in workforce management.
The priorities were:
-
Automating attendance and payroll activities
-
Tracking absences, leaves, and terminations
-
Detecting and rejecting errors in timecards
-
Linking labor costs to individual projects
-
Generating customized reports on demand
FirstBit ERP was implemented to cover all these areas through its
HR and payroll module. Most manual tasks were automated, reports could be created instantly, and attendance records were validated without errors.
According to Rashid Khawaja, HR Manager at KKC, the system not only saved time and resources but also made managing the workforce more efficient. He highlighted the flexibility of FirstBit ERP in adapting to their contracting environment and praised the support team for resolving issues quickly.
Takeaway
UAE 2025 mega projects represent a shift in urban mobility — moving away from car dominance toward a greener, community-oriented transportation model. By integrating cycling infrastructure with social amenities like urban agriculture and climate-resilient design, the initiative reinforces Dubai’s commitment to sustainable, livable, and resilient city planning.
This vision is part of a broader trend across the Gulf, where
major cities are using mega projects not only to expand capacity but also to redefine how urban growth aligns with sustainability and long-term resilience.
Stay one step ahead of competitors
Request a demo