The types of construction contracts used on a project determine how costs, risks, responsibilities, and timelines are managed from day one. In the UAE, where projects often involve multiple stakeholders, authorities, and fast-tracked schedules, this choice carries direct commercial impact.
Selecting the wrong construction contract can expose owners to budget uncertainty and delay disputes. For contractors, it can shift financial and legal risks, affecting cash flow and long-term viability.
Understanding what is a construction contract is and how the different types of construction contracts operate in practice helps project teams make informed procurement decisions before work begins.
What Is a Construction Contract
A construction contract is a legally binding agreement that governs how a construction project is executed. It sets out the scope of work, payment structure, timelines, responsibilities, and legal rights of all parties involved.
In the UAE, a construction contract also defines compliance with local regulations, authority approvals, and dispute resolution mechanisms. It is both a commercial and legal document that controls how the project operates in practice.
Construction contracts under UAE law fall within Articles 872–896 of the UAE Civil Code — the so-called “muqawala” contracts — which are generic contracts to make something or to perform a task as stated in Art. 872 [?] .
When people ask what is a construction contract, the practical answer is simple. It is the document that determines who carries cost risk, who manages design responsibility, and how changes are priced and approved.
The form of the construction contract directly affects project cash flow, claim exposure, and delay risk. This is why selecting from the different types of construction contracts at the tender stage is a strategic decision rather than a procedural step.
In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the most commonly used standard form for construction contracts is the Fédération Internationale des Ingénieurs-Conseils (FIDIC) suite. FIDIC contracts can be used for construction-only projects or for combined design-and-construction projects [?] .
Different Types of Construction Contracts in UAE
The types of construction contracts in UAE reflect the diversity of projects delivered across residential, commercial, infrastructure, and industrial sectors. From private developments to large public works, contract selection directly influences cost certainty, risk exposure, and project control.
Unlike markets that rely heavily on one dominant model, the UAE applies several different types of construction contracts based on funding structure, procurement strategy, and regulatory requirements. Each construction contract shifts commercial and legal responsibility in different ways.
In 2024, construction output in the UAE reached USD 107.2 billion, reflecting the scale and financial exposure tied to contract decisions across the sector [?] .
As project values rise, the structure of the construction contract becomes more critical. Large developments often involve layered contracts,
multiple subcontractors, and complex risk-sharing mechanisms.
Understanding what are the types of contract in construction allows owners and contractors to match legal structure with commercial priorities. Some projects require strict cost certainty, while others need flexibility to absorb change during execution.
The most commonly used types of construction contracts in the UAE include:
Lump Sum or Fixed Price Contracts
Unit Price Contracts
Cost-Plus or Cost Reimbursable Contracts
Time and Materials (T&M) Contracts
Design-Build Contracts
Turnkey Contracts
EPC Construction Contracts
Each of these different types of construction contracts serves a specific purpose depending on scope clarity, risk tolerance, and delivery responsibility.
Lump Sum or Fixed Price Construction Contracts
A lump-sum arrangement is one of the most commonly used types of construction contracts in the UAE. Under this model, the contractor agrees to complete the full scope of work for a fixed total price defined at the time of signing.
This construction contract is typically used when design documents are complete, quantities are clear, and the project scope is unlikely to change during execution.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides full cost certainty to the owner from the outset. | Variations can lead to disputes if the original scope is not clearly defined. |
| Simplifies budgeting, financing, and cash flow planning. | Contractors often price in higher risk premiums, increasing initial bid values. |
| Transfers most cost overrun risk to the contractor. | Incomplete designs at the tender stage increase claim exposure for both parties. |
| Administrative control is simpler with milestone-based payments. | Limited flexibility for scope changes during project execution. |
Unit Price Construction Contracts
A unit price model is a construction contract where work is paid based on measured quantities at agreed unit rates. The final contract value depends on the actual quantities executed on site.
This is one of the different types of construction contracts commonly used when the scope is generally defined, but exact quantities cannot be confirmed at the tender stage. It is widely applied in infrastructure, utilities, and earthworks projects across the UAE.
Under this construction contract, the employer carries greater quantity risk, while the contractor carries performance and productivity risk.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides flexibility when quantities cannot be accurately determined upfront. | Final project cost is uncertain at contract signing. |
| Reduces the need for excessive risk loading in tender pricing. | Employers carry the risk of quantity overruns. |
| Allows fair valuation of variations based on actual measured work. | Requires strong site measurement and cost control systems. |
| Well-suited for roadworks, pipelines, and infrastructure projects. | Disputes may arise from quantity measurement and re-measurement. |
Cost-Plus or Cost Reimbursable Construction Contracts
A cost-plus model is a construction contract where the contractor is reimbursed for actual project costs, along with an agreed fee or percentage for overhead and profit.
This is one of the different types of construction contracts used when the project scope is not fully defined, or when work must begin before final designs are completed. It is often applied to fast-track, emergency, or specialist projects in the UAE.
Under this construction contract, cost transparency becomes critical, as payments are based on verified expenses rather than predetermined prices.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Allows work to start quickly even when the design is incomplete. | Final project cost is uncertain and can escalate without strict controls. |
| Reduces pricing risk for contractors. | Employers carry most of the cost overrun risk. |
| Transparent cost structure when supported by proper documentation. | Requires rigorous auditing and financial monitoring. |
| Suitable for complex or evolving project scopes. | Less incentive for the contractor to control costs without incentive clauses. |
Time and Materials (T&M) Construction Contracts
A time and materials model is a construction contract where the employer pays the contractor based on actual labor hours worked and the cost of materials used, plus an agreed markup.
This approach is one of the different types of construction contracts used when the scope cannot be clearly defined at the outset, or when frequent changes are expected during execution.
In the UAE, this construction contract is often applied to maintenance works, retrofit projects, and short-term specialist services.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Offers maximum flexibility when the scope is uncertain. | The final project cost is difficult to predict at the start. |
| Enables fast mobilization without waiting for full design details. | Employers carry most of the cost risk. |
| Suitable for repair, maintenance, and specialist works. | Requires continuous supervision of labor and material usage. |
| Reduces pricing pressure on contractors at the tender stage. | Inefficient work practices can inflate project costs. |
Design-Build Construction Contracts
A design-build model is a construction contract where a single entity is responsible for both the design and construction of the project. The employer deals with one party for delivery instead of separate designers and contractors.
This is one of the types of construction contracts in UAE commonly used for fast-track projects where time certainty and single-point responsibility are priorities.
Under this construction contract, design and construction risks are combined under a single party.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Single point of responsibility for design and construction. | The employer has less direct control over detailed design decisions. |
| Shorter project timelines due to overlapping design and construction phases. | Design changes after the award can be costly. |
| Reduced coordination issues between the designer and contractor. | Requires clear performance specifications at the contract stage. |
| Improved accountability for time and cost outcomes. | Employers depend heavily on the design-build contractor’s competency. |
Turnkey Construction Contracts
A turnkey construction contract requires the contractor to deliver a fully completed and operational facility to the employer. The contractor is responsible for design, construction, procurement, and commissioning until the project is ready for use.
This is one of the types of construction contracts in UAE commonly used for industrial facilities, commercial buildings, and certain infrastructure projects where the owner prefers minimal involvement during execution.
Under this construction contract, the employer hands over most delivery responsibility to a single party and receives a “ready-to-use” asset at completion.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Single entity responsible for the full project lifecycle. | Limited control for the employer during design and execution. |
| Clear handover of a fully functional facility at completion. | Design changes after contract award are difficult and costly. |
| Reduced coordination effort for the employer. | High reliance on the contractor’s technical and financial capacity. |
| Suitable for clients seeking minimal operational involvement. | Premium pricing may apply due to the high risk borne by the contractor. |
EPC Construction Contracts
An EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) construction contract places responsibility for engineering design, material procurement, and construction execution under one contractor. Unlike a pure turnkey model, EPC contracts often include stricter performance guarantees and testing obligations before final handover.
This is one of the types of construction contracts in UAE widely used for power plants, oil and gas facilities, water treatment plants, and large industrial projects where technical performance is critical.
Under an EPC construction contract, the contractor usually carries full responsibility for cost, time, and performance delivery in accordance with defined specifications.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Single point of responsibility for engineering, procurement, and construction. | Higher contract value due to extensive risk transfer to the contractor. |
| Strong performance guarantees and testing before handover. | Limited flexibility for design changes after contract award. |
| Fixed completion timelines with clear delay accountability. | Complex contract administration and strict compliance requirements. |
| Reduced interface risk for the employer. | The employer has less control over procurement choices. |
Navigate UAE construction laws with an ERP built for the UAE market
Request a demo
How to Choose the Right Construction Contract for Your Project
Steps to choose the right construction contract
Selecting the right construction contract is a commercial decision that affects cost certainty, legal exposure, and project control throughout the lifecycle of a project.
The choice is rarely based on one factor alone. It depends on scope clarity, financial structure, risk tolerance, regulatory requirements, and delivery timelines. Understanding how these variables interact helps project owners and contractors align contract strategy with execution reality.
Assessing Project Scope and Complexity
Project scope is the primary driver when deciding between the different types of construction contracts. A clearly defined scope supports fixed-price models, while evolving scopes require more flexible arrangements.
Projects with well-developed designs and stable quantities are better suited to lump sum or EPC construction contracts. These models rely on design certainty to function effectively.
Complex or fast-track projects with incomplete designs at the tender stage often require cost-plus or time and materials structures. These allow work to proceed while details are still being refined.
The more ambiguous the scope, the greater the need for flexibility within the construction contract. However, increased flexibility also increases cost uncertainty and monitoring requirements.
Cost Predictability vs Flexibility
Cost predictability and flexibility sit on opposite ends of the contract spectrum. Most types of construction contracts balance these two factors in different ways. Lump sum and EPC construction contracts offer high cost certainty. The total project price is largely fixed at contract signing, which supports financing and long-term budgeting.
However, this predictability comes with limited flexibility. Any post-award change typically results in variations that affect both cost and time.
Cost-plus and time and materials models provide maximum flexibility. They allow design evolution and scope changes without renegotiating the entire construction contract. The trade-off is reduced cost certainty. Employers must rely on strict cost monitoring and approval controls to prevent budget overruns.
Unit price contracts sit between these two extremes. They allow flexibility in quantities while maintaining pricing control through agreed unit rates.
Risk Allocation & Responsibility
Risk allocation is one of the most defining factors across the types of construction contracts. Each construction contract shifts cost, time, and performance risk differently between the employer and the contractor.
Under lump sum and EPC contracts, most financial and delay risk is transferred to the contractor. The employer benefits from cost and time certainty, provided the scope is clearly defined.
In cost-plus and time and materials models, the employer retains most cost risk. The contractor is protected from price volatility, but the employer must actively control spending. Unit price contracts distribute risk more evenly. The contractor carries productivity risk, while the employer carries quantity risk based on actual site measurements.
Design-build, turnkey, and EPC contracts also transfer design responsibility to the contractor. This reduces interface risk for the employer but increases reliance on the contractor’s technical capability.
Understanding how a construction contract allocates risk helps both parties price the project correctly and avoid disputes during execution.
Legal or Regulatory Considerations in the UAE
Legal and regulatory requirements in the UAE influence how a construction contract is drafted, interpreted, and enforced. These factors must be considered alongside commercial terms when selecting from the types of construction contracts.
Many contracts in the UAE are required to be executed in Arabic or accompanied by an Arabic translation. In disputes, the Arabic version typically prevails before local courts.
Governing law is another key consideration. Most types of construction contracts in UAE are governed by
UAE civil law, with provisions drawn from the UAE Civil Code and Commercial Transactions Law.
Dispute resolution mechanisms must be clearly defined within the construction contract. Arbitration is widely used for large projects, while smaller disputes may proceed through local courts or mediation.
Regulatory compliance with municipal authorities, free zone regulations, and sector-specific bodies must also be embedded into contract obligations. Failure to align the contract with local regulatory frameworks can delay approvals and expose both parties to legal risk.
Best Practices for All Types of Construction Contracts in UAE
Best practices in contract management go beyond selecting the right model. They focus on how the construction contract is drafted, administered, and enforced throughout the project lifecycle.
Even well-chosen contract types can fail if the scope definition is weak, the documentation is inconsistent, or change management is poorly controlled.
Applying disciplined contract practices reduces dispute risk and improves cost, time, and quality outcomes across all types of construction contracts in UAE.
Contract Drafting and Adaptation for UAE
Effective contract drafting starts with a clearly defined scope of work. Ambiguity at this stage leads to variations, claims, and delay disputes during execution.
Payment terms must align with project cash flow cycles. This includes milestone definitions, certification procedures, retention, and final account settlement.
Defect liability periods, warranties, and performance guarantees must be expressly stated in the construction contract. These clauses directly affect post-handover risk and maintenance responsibilities.
Standard form contracts are often used as a base. However, they must be adapted to reflect UAE legal requirements, authority approvals, and local enforcement practices. Failure to localize standard forms can create gaps between contractual intent and legal enforceability under UAE law.
Documentation and Change Management
Effective documentation is essential for controlling variations across all types of construction contracts in UAE. Every instruction, approval, and modification must be formally recorded to prevent later disputes.
Change orders should clearly define the revised scope, cost impact, and time adjustment. Verbal instructions without written confirmation often become the source of contractual conflict.
Accurate records of drawings, site instructions, measurements, and interim payments support fair valuation under any construction contract. This is especially critical for unit price, cost-plus, and T&M models.
A
structured change management process helps both parties track commercial impact in real time. Without it, minor adjustments can accumulate into significant budget exposure.
Strong documentation practices protect cash flow, simplify final account settlement, and strengthen legal position in the event of a dispute.
Dispute Resolution and Governing Law
Dispute resolution provisions play a critical role across all types of construction contracts in UAE. These clauses determine how conflicts are resolved when commercial or technical disagreements arise.
Most large UAE construction contracts include arbitration as the primary dispute resolution mechanism
[?] . Arbitration offers confidentiality, technical expertise, and enforceability under international conventions.
Litigation through local courts is more common in smaller projects or where arbitration is not contractually agreed upon. Court proceedings follow UAE civil law procedures and can be time-consuming.
Pro tip: Mediation is increasingly used as an early-stage dispute avoidance tool. It allows parties to resolve issues without escalating to formal legal proceedings.
Clear governing law clauses are essential in every construction contract. Ambiguity over applicable law can complicate enforcement and increase legal costs during disputes.
Insurance and Risk Mitigation
Insurance is a core risk management tool across all types of construction contracts in UAE. It protects both the employer and the contractor from financial exposure arising from accidents, design errors, and third-party claims.
Contract works all-risk insurance is typically required to cover physical damage to the project during construction. This policy often extends to temporary works, plants, and equipment used on site.
Professional indemnity insurance is critical for contracts involving design responsibility, such as design-build, turnkey, and EPC construction contracts. It covers errors or omissions in professional services.
Decennial liability insurance is a statutory requirement in the UAE for structural defects affecting building safety. It provides long-term protection to owners for major construction failures after completion.
Note: Clear allocation of insurance obligations within the construction contract prevents coverage gaps. Without this clarity, parties may assume protection that does not legally exist.
Working with Contractors or Consultants and Selecting Partners
Selecting the right delivery partner is as critical as choosing the right construction contract. Technical capability, financial stability, and past performance directly affect project outcomes.
Contractors with experience under specific types of construction contracts in UAE are better equipped to manage the associated risks and administrative requirements. A strong track record in similar projects reduces execution uncertainty.
Consultants play a key role in scope definition, contract administration, and certification. Their competence directly influences variation control, payment accuracy, and dispute avoidance. Due diligence should extend beyond price comparisons. Evaluating resources, safety history, claims record, and regulatory compliance capability helps prevent downstream project failure.
Clear alignment between contract type, project complexity, and partner capability creates a stronger foundation for cost control, timely delivery, and reduced legal exposure.
Start your UAE construction business with confidence
Request a demo
How FirstBit ERP Streamlines Construction Contract Management in the UAE
Managing different types of construction contracts in UAE requires tight control over costs, variations, and cash flow. As project values increase, even small gaps in documentation or financial tracking can create significant commercial risk.
FirstBit ERP supports contract management by integrating core financial and procurement controls within a structured system. It does not alter contractual terms but helps enforce the financial discipline required under each construction contract.
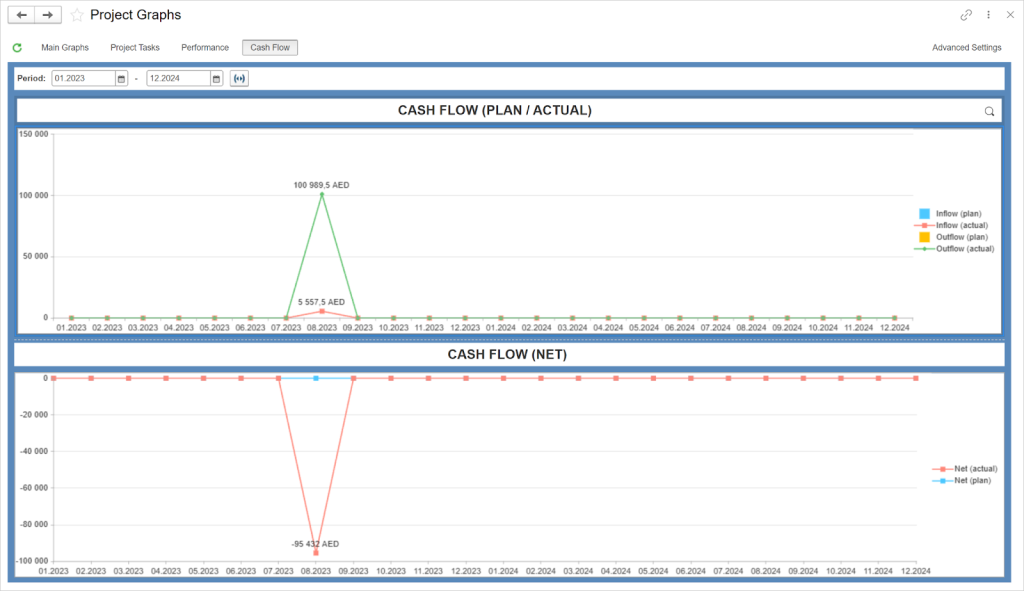
Centralized contract and financial control. Project costs, procurement data, and financial records are maintained within one system. This allows consistent oversight across multiple construction contracts without relying on disconnected spreadsheets or manual logs.
Contract value, cost, and budget tracking. Contract values, committed costs, and actual expenditures can be tracked together. This provides clear visibility of financial exposure under each construction contract.
Cash Flow Graphs in FirstBit ERP
Variation and change order control. Approved variations can be recorded as structured adjustments to contract values and budgets. This helps maintain an accurate financial position when scope changes occur.
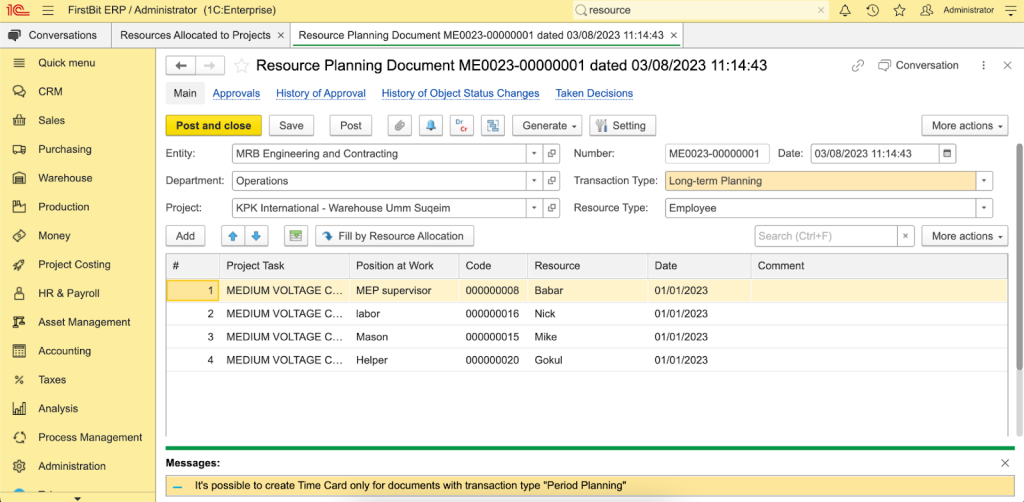
Procurement is aligned with contract budgets. Purchase orders and supplier billing are linked to approved project budgets. This helps prevent uncontrolled spending beyond contractual limits.
Resource Planning Document in FirstBit ERP
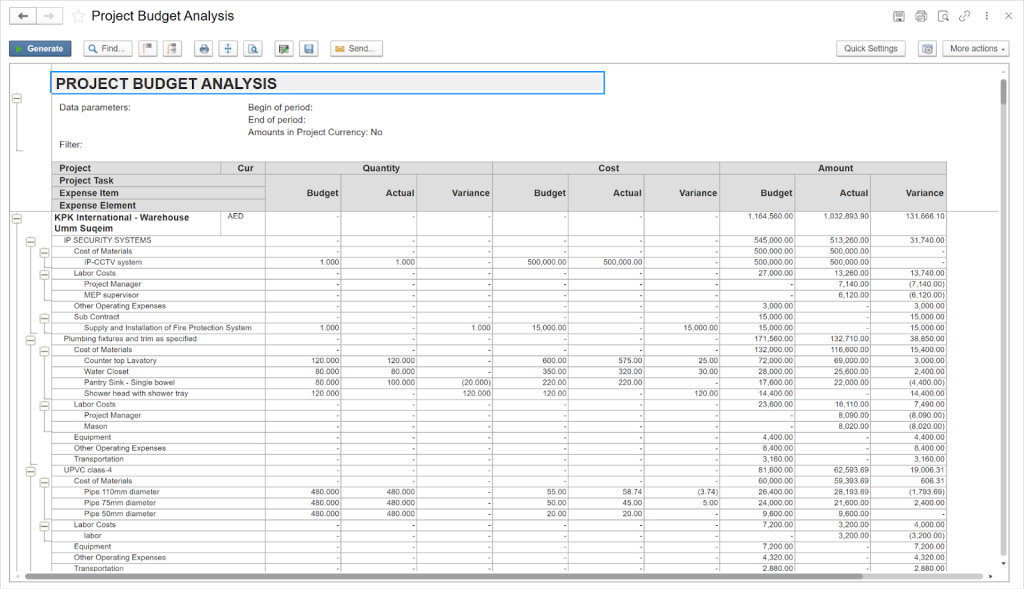
Project-wise financial reporting and cash flow visibility. Cost, revenue, and margin reports can be generated at the project level across different types of construction contracts. These reports support commercial review and informed management decisions.
Project Budget Analysis in FirstBit ERP
By structuring financial and procurement data around the construction contract, ERP-based controls help reduce commercial leakages and improve transparency. This becomes especially important when managing multiple projects under different contract models simultaneously.
Conclusion
Choosing from the types of construction contracts is not a procedural step. It is a strategic decision that directly influences cost certainty, risk exposure, cash flow stability, and dispute likelihood across a project.
In the UAE, where projects often involve high capital value and layered stakeholder structures, the construction contract defines how commercial pressure is distributed across the project lifecycle. A mismatch between contract type and project realities frequently becomes the root cause of claims and delays.
Understanding what a construction contract is and how the different types of construction contracts in UAE operate allows project owners and contractors to align legal structure with commercial intent. Fixed-price models suit stable scopes, while flexible models support evolving designs.
No single contract type is ideal for every project. The right choice depends on scope clarity, funding structure, risk tolerance, and regulatory context.
Use an ERP compliant with UAE laws
Operate confidently in the UAE regulatory landscape
Request a demo
FAQ
What are the four types of construction contracts?
The four most commonly recognized primary types of construction contracts are the Stipulated Sum (Lump Sum) Contract, Cost Plus Contract, Design-Build Contract, and the Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) Contract. Each differs in how cost, risk, and responsibility are allocated between parties.
What is the construction contract?
A construction contract is a legally binding agreement that defines the scope of work, pricing method, timelines, responsibilities, deliverables, and legal rights of both the contractor and the employer.
What are the 7 basic elements of a contract?
The seven basic elements of a contract are offer, acceptance, consideration, legally competent parties, mutual consent, clear terms, and a lawful purpose.
Umme Aimon Shabbir
Editor at First Bit
Aimon brings a deep understanding of the modern construction business to her articles by providing practical content.