Imagine this: you’re halfway through a project, and suddenly everything feels like it’s falling apart. Deadlines are slipping, tasks are overlapping, and you’re constantly putting out fires instead of making progress. Sound familiar? You’re not alone.
Studies show that 70% of projects miss their deadlines due to poor planning and scheduling[?]— and it’s one of the biggest frustrations for project managers.
But here’s the good news: the Critical Path Method (CPM) can help you take back control. By pinpointing the tasks that matter most and mapping out the most efficient route to your goals, CPM helps you tackle even the most complex projects with clarity and confidence.
In this guide, we’ll break down CPM in simple terms — what it is, why it works, and how you can use it to stay on top of your projects. No more missed deadlines or last-minute panic. We’ll help you turn confusion into clarity and get your projects running smoothly from start to finish. Let’s get started!
What is CPM (Critical Path Method)?
The Critical Path Method, or CPM, is like a roadmap for your project. It helps you figure out the most important tasks — the ones that absolutely need to be finished on time for the whole project to stay on track. Think of it as a way to find the shortest and most efficient route to get your project done.
Here’s how CPM works:
-
Every project has tasks. Whether you're building a house, managing a construction site, or working on a small renovation, there are multiple tasks that need to happen. And some tasks depend on others to be completed first. For example, you can’t paint a wall until it’s built, right?
-
CPM organizes these tasks. It lays out all the steps in your project, showing which ones need to be done first and which can happen at the same time. It’s like lining up dominoes — you need to set them up in the right order to get the final result.
-
It identifies the “critical path.” This is the longest chain of tasks that must be done on schedule. If one task on this path is delayed, the whole project is delayed. For example, if you’re waiting for concrete to dry before moving to the next step, that task is on your critical path.
-
It shows you where you have wiggle room. Not all tasks are critical. Some can be delayed without affecting the overall timeline. CPM helps you see which tasks can wait and which ones can’t.
Why CPM is a Game-Changer in Construction Projects
The Critical Path Method (CPM) isn’t just another project management tool; it’s a total game-changer, especially for construction projects where every day counts and delays can cost a fortune.
Let’s break down why CPM is so powerful and how it can transform the way you manage your projects.
1. Streamlined Project Timelines
One of the biggest headaches in construction is figuring out how long the project will take. With CPM, you don’t have to guess. It lays out every task in order, shows which ones depend on others, and highlights the critical functions that must be finished on time.
Focusing on the critical path lets you know exactly which tasks to prioritize to keep the project moving forward. This means no wasted time, guessing games, or last-minute surprises.
2. Effective Resource Allocation
Construction projects rely on a lot of moving parts — workers, equipment, and materials — and it’s easy to waste resources if you’re not careful. CPM helps you see what’s needed, when it’s needed, and where it’s needed.
For example:
-
You’ll know when to schedule workers, so they’re not standing around waiting for materials.
-
You’ll avoid renting expensive equipment too early or too late.
3. Proactive Risk Identification and Mitigation
Construction projects are full of risks. Weather delays, material shortages, or unexpected site issues can throw your timeline off. CPM helps you spot potential risks before they become major problems.
How? By showing you the critical tasks and how delays in one area could impact the whole project. Once you know the risks, you can create backup plans, adjust schedules, or shift resources to stay on track.
4. Improved Communication and Accountability
CPM doesn’t just make planning easier — it also makes it easier to keep everyone on the same page. When you share the project timeline with your team, subcontractors, and clients, everyone knows what’s expected and when.
This clarity:
-
Reduces miscommunication
-
Keeps everyone accountable for their part of the project
-
Helps you manage expectations with clients and stakeholders
5. Better Decision-Making
When challenges come up (and they always do), CPM gives you the information you need to make smart decisions. Should you move workers to another task? Will a delay in one area affect the whole project? With CPM, you’ll have the answers, so you can act quickly and keep things moving.
Step-by-Step Process of Implementing CPM
Implementing the Critical Path Method (CPM) may sound technical, but it’s actually a straightforward process when broken down into clear steps. Think of it like building a blueprint for your project.
1. Setting Up The Framework
Before you start using CPM, you need to set up a solid foundation. This involves gathering all the details about your project, such as its overall goal, scope, and resources. Think about what you want to achieve and the tasks required to get there. Once you have a clear understanding of the project’s big picture, you can start breaking it into smaller, actionable steps.
2. Break Down Your Project into Tasks
Every project is made up of smaller tasks, each contributing to the final goal. Start by listing all the tasks involved in your project. Be as detailed as possible — missing a step now could lead to problems later.
For example, if you’re managing a home construction project, your tasks might include:
-
Clearing the site
-
Pouring the foundation
-
Framing the structure
-
Installing electrical systems
This step is all about creating a complete checklist of everything that needs to be done.
3. Figure Out Task Dependencies
Once you’ve listed all your tasks, figure out how they connect to each other. Some tasks can only start after others are finished, while some can run at the same time. These relationships are called dependencies.
For example:
-
You can’t install windows until the walls are framed.
-
Plumbing and electrical work can happen simultaneously in different parts of the structure.
Understanding these dependencies helps you sequence the tasks correctly and avoid unnecessary delays.
4. Assign Time Estimates
Next, estimate how long each task will take. Be realistic here — underestimating can throw off your entire schedule. Consider factors like:
-
The complexity of the task
-
Availability of resources (workers, equipment, materials)
-
Potential risks or delays, like bad weather
For example, pouring a foundation might take three days, while installing plumbing could take a week. These time estimates will form the backbone of your schedule.
5. The Forward Pass (Determine Earliest Start & Finish Times)
Now, it’s time to calculate when each task can start and finish, assuming everything goes perfectly. Start from the first task and move forward, adding up the time estimates as you go. This gives you the earliest start time (ES) and earliest finish time (EF) for each task.
For example:
Task 1: Start on Day 1, finish on Day 3 (ES = Day 1, EF = Day 3).
Task 2 (depends on Task 1): Start on Day 4, finish on Day 6 (ES = Day 4, EF = Day 6).
This step gives you a sense of how quickly the project can be completed if everything runs smoothly.
6. The Backward Pass (Determine Latest Start & Finish Times)
Now, work backward from the project deadline to calculate the latest start time (LS) and latest finish time (LF) for each task. This step shows you how much flexibility you have for each task.
For example: If Task 2 must be finished by Day 10, and it takes 3 days, the latest it can start is Day 7 (LS = Day 7, LF = Day 10).
This backward pass ensures you know the latest possible time to start or finish a task without delaying the overall project.
7. Calculate Slack Time
Slack time (or float) is the extra time a task can be delayed without impacting the overall project timeline. Tasks with no slack are critical — they’re part of the critical path, and any delay in these tasks will delay the entire project.
For example: If Task 2 has an earliest start time of Day 4 and a latest start time of Day 7, it has 3 days of slack (LS - ES = Slack).
Identifying slack time helps you focus on the tasks that matter most.
8. Identify the Critical Path
Finally, identify the critical path — the longest sequence of tasks with no slack. These are the tasks that must be completed on time for the project to stay on schedule.
For example, if the critical path is Task 1 → Task 2 → Task 5, you know these tasks require your full attention and resources. Any delay here will delay the entire project.
Challenges and Limitations of CPM
While the Critical Path Method (CPM) is a powerful tool for managing projects, it’s not without its challenges. Understanding its limitations will help you use it more effectively and avoid potential pitfalls.
1. Estimating Accurate Task Duration
One of the biggest challenges with CPM is accurately estimating how long each task will take. If your time estimates are off, the entire critical path can be thrown out of sync.
For example, if you underestimate the time needed to pour and cure concrete, subsequent tasks like framing might start later than planned, causing delays across the board.
How to manage this challenge:
-
Use historical data from similar projects to inform your estimates.
-
Consult with experienced team members or subcontractors who can provide realistic timelines.
-
Build a buffer for tasks with high uncertainty.
2. Limited Adaptability to Evolving Project Needs
Construction projects rarely go exactly as planned. Unexpected changes — like design adjustments, weather delays, or material shortages — can disrupt your carefully mapped-out critical path. CPM isn’t inherently flexible, making it harder to adapt to evolving project needs.
For example, if a client requests a change in the building layout midway through the project, your original timeline might no longer apply.
How to manage this challenge:
-
Regularly update your CPM schedule as changes occur.
-
Use CPM alongside other tools, like Agile or rolling-wave planning, for more flexibility.
-
Communicate changes quickly to all stakeholders and adjust timelines accordingly.
3. Resource Availability Assumptions
CPM assumes that all necessary resources like labor, materials, and equipment will be available when needed. In reality, resource availability can fluctuate, causing delays that aren’t accounted for in the initial CPM plan.
For example, if a critical piece of equipment is delayed or workers are unavailable due to another project, tasks on the critical path might be stalled.
How to manage this challenge:
-
Include resource planning as part of your CPM process.
-
Work closely with suppliers and subcontractors to ensure resources are scheduled in advance.
-
Have backup plans for critical resources, like alternative suppliers or rental options for equipment.
4. Managing Interdependent Tasks in Complex Scenarios
In large construction projects, tasks are often highly interdependent, meaning a delay in one task can create a domino effect. This complexity can make it challenging to manage and adjust the critical path, especially when multiple teams are involved.
For example, if electrical work is delayed, it might impact plumbing, drywall installation, and finishing tasks, creating bottlenecks across the project.
How to manage this challenge:
-
Break the project into smaller phases or sections to simplify interdependencies.
-
Use project management software to visualize and track these relationships in real-time.
-
Conduct regular progress reviews to identify and address potential bottlenecks early.
How FirstBit ERP Optimizes CPM for Efficient Project Management
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a powerful way to streamline project timelines, but manually managing all the tasks, dependencies, and resources can be overwhelming. That’s where FirstBit ERP steps in to make the process faster, easier, and more accurate.
By integrating CPM with smart tools and automation, FirstBit ERP helps you focus on delivering your projects on time and within budget.
-
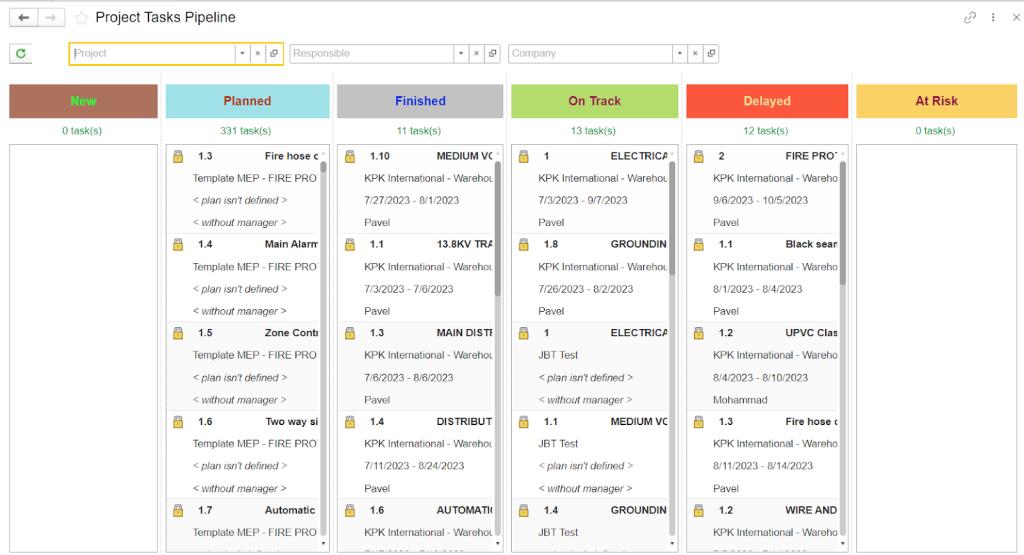
Simplified task management. FirstBit ERP makes it easy to break down your project into tasks and subtasks, organizing them by priority or phase. You can assign each task to the right team member or subcontractor, ensuring every responsibility is clear and centralized for better tracking and management.
-
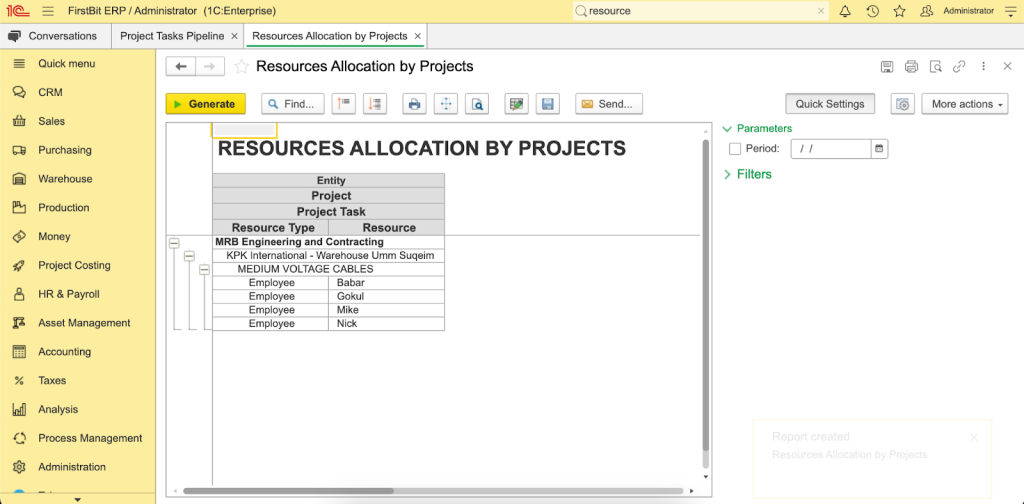
Accurate time and resource planning. The platform allows you to create precise timelines using historical data and real-time resource availability. You’ll receive alerts for potential delays or resource conflicts, helping you optimize resource allocation and keep the project running smoothly without downtime.
-
Real-time monitoring and updates. With FirstBit ERP, you can monitor progress in real-time, identifying which tasks are on schedule and which are delayed. The platform shows how delays impact the critical path and overall timeline, enabling you to adjust plans quickly and address issues before they escalate.
-
Enhanced collaboration and communication. The platform centralizes communication, allowing all teams, subcontractors, and stakeholders to stay aligned. Shared project timelines, automated notifications for updates, and customizable dashboards ensure everyone is informed and on the same page, reducing misunderstandings and delays.

Umme Aimon Shabbir
Editor at First Bit

See FirstBit ERP solutions in action
Discover how our system solves the unique challenges of contractors in a personalized demo.
After the demo you will get a quotation for your company.
After the demo you will get a quotation for your company.