Implementing an ERP system isn’t just about installing software. It’s a major business decision that impacts every part of your organization. Done right, it can streamline operations, boost productivity, and give leaders the insights they need to make smarter decisions. But it’s not something that happens overnight.
ERP implementation is a multi-phase process, and each phase brings its own set of challenges. Without the right planning and execution, it’s easy to run into delays, low user adoption, or worse, complete project failure.
In this article, we’ll walk through the five crucial phases of ERP implementation, detailing what each phase entails, how to navigate potential pitfalls, and why FirstBit is the ideal partner to help guide you through this intricate process.
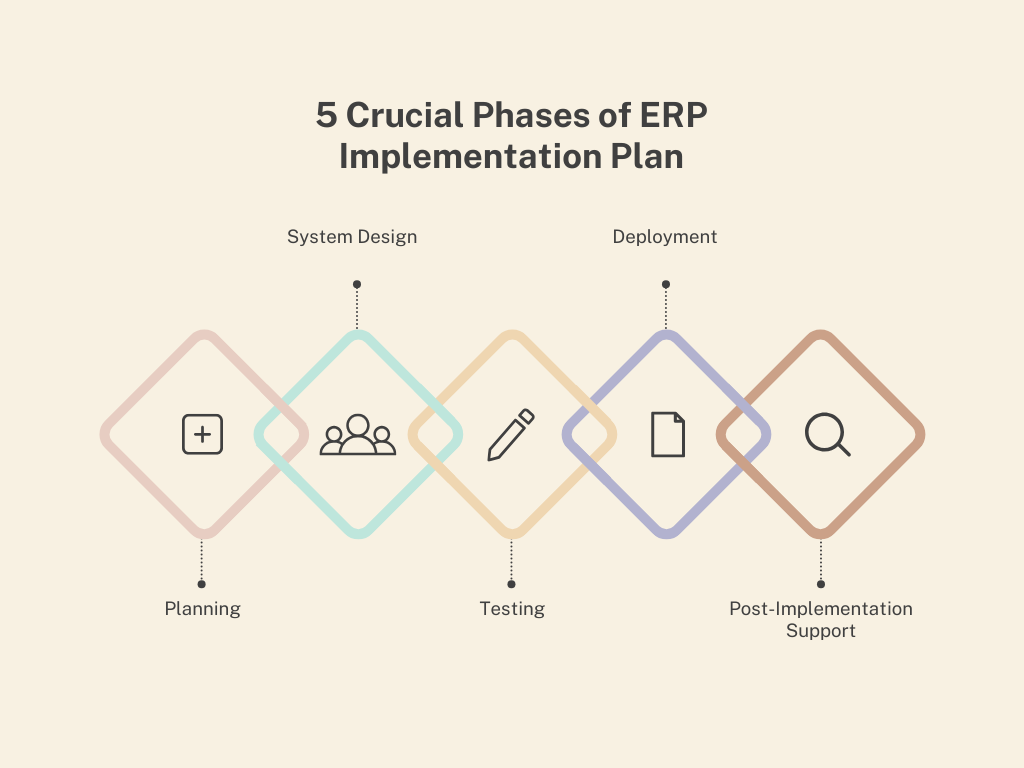
5 Phases of ERP Implementation
Phase 1: Planning
The planning phase is the foundation for a successful ERP implementation. This stage lays out the blueprint for the entire project by defining business objectives, setting expectations, and identifying potential risks.
According to the 2020 ERP Report by Panorama Consulting Solutions, around 50% of ERP implementations experience delays, and more than 60% fail to meet their initial expectations due to poor planning and insufficient resources.[?]
This highlights why investing time and resources in thorough planning is key to a successful ERP implementation.
Defining Business Requirements
The first step in the planning phase is to clearly identify your business requirements. Engaging with key stakeholders across various departments helps ensure the ERP system meets everyone’s needs. This involves creating a detailed list of features, workflows, and integrations that will be required from the ERP solution.
According to PwC, organizations that involve cross-functional teams in their ERP projects are 1.5 times more likely to complete the project on time and within budget.[?]
Assembling the Project Team
The next critical task is to assemble the project team. This team should include individuals from IT, finance, operations, and other key departments. Additionally, it is essential to bring in ERP consultants or vendors with experience in your industry. Having the right team in place at the start ensures that the project stays on track and challenges are addressed promptly.
Setting Realistic Timelines and Budget
A well-planned ERP implementation requires realistic timelines and budget allocations. While it’s tempting to set aggressive goals, setting unrealistic timelines and underestimating resource needs can lead to project failure. By budgeting appropriately and allowing for buffer time, businesses can ensure smoother execution.
Phase 2: System Design
The system design phase is where the blueprint of the ERP system is created. During this phase, businesses define the system's architecture and ensure that it aligns with existing business processes and future growth. This phase focuses on customization, integration, and overall design.
Designing the Architecture
Designing the system’s architecture is critical for
scalability and flexibility. This step ensures the ERP system can handle both current operations and future demands. Companies should work closely with their ERP vendor to design a system that integrates seamlessly with other business tools and processes.
Customizing the ERP System
Once the architecture is in place, customization follows. Since every business has unique needs, the ERP system often needs to be tailored to fit specific workflows. Customizations might include adjusting the user interface or modifying core features to better serve business requirements.
Integration with Existing Systems
One of the biggest challenges of the system design phase is ensuring the ERP system integrates smoothly with other existing applications, such as customer relationship management (CRM) or legacy systems. Poor integration can lead to data discrepancies and workflow disruptions, which can significantly hamper the system's effectiveness.
Gain full control of your business
Get a 360° project view with FirstBit ERP
Request a demo
Phase 3: Testing
Testing is a pivotal phase that involves validating the ERP system’s functionality, performance, and usability. Companies that fail to conduct thorough testing during the implementation phase are at risk of overlooking key issues that may only surface post-implementation.
Unit Testing
Unit testing involves testing individual components or modules of the ERP system to ensure they are functioning correctly. For example, testing financial management functions, payroll processes, and inventory controls ensures each system performs as required.
Integration Testing
After unit testing, integration testing ensures that the different modules of the ERP system work together as expected. This phase verifies that data flows smoothly between modules and external systems.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is arguably the most critical form of testing. It involves the actual end-users testing the system to ensure it meets their requirements.
According to Deloitte, companies that conduct thorough UAT are 73% more likely to achieve higher adoption rates post-implementation.[?]
This phase gives users the chance to identify any usability issues and refine workflows before the system goes live.
Phase 4: Deployment
Deployment is when the ERP system is officially introduced into the business environment. This phase can be stressful if not executed carefully. A smooth deployment can minimize downtime and ensure the organization can quickly adapt to the new system.
According to Panorama, Structured deployment plans result in 50% fewer post-implementation issues.[?]
Deployment Planning and Rollout Strategy
A successful deployment starts with careful planning. Businesses must decide between a "big bang" approach, where everything is rolled out at once, or a phased approach, where the system is introduced gradually. The rollout strategy should consider any risks, such as potential system downtime or initial user confusion.
A key element of deployment planning is ensuring proper communication. Everyone involved should know the timeline, their roles, and expectations. Having a solid backup and rollback plan is essential in case there are any unforeseen challenges or failures after going live.
Final Data Migration
Once the system design and testing phases are complete, the final data migration takes place. This step involves transferring all clean, validated data from the old system into the new ERP. It’s critical to ensure that data is intact, error-free, and fully integrated into the new system. This step is usually performed in a controlled manner, often after hours, to minimize disruption to business operations.
End-User Training and Support Setup
Training is an essential part of the deployment phase. Employees need to understand how to use the new system effectively. Comprehensive training sessions cover everything from system navigation to handling common workflows.
In addition to training, having a robust support system in place is crucial. A dedicated helpdesk or support team should be available to address any immediate technical or user issues that arise once the system is live.
Everything you need for success in one powerful ERP solution
Request a demo
Phase 5: Post-Implementation Support
The post-implementation phase is where many ERP projects falter. Without ongoing support and optimization, an ERP system can become outdated or fail to meet evolving business needs.
In fact, 60% of ERP failures are attributed to insufficient post-implementation support.[?]
It’s crucial to have a comprehensive support structure in place to address any challenges and ensure the system remains aligned with business goals.
Monitoring System Performance and Error Resolution
System performance monitoring is crucial after deployment. Teams should keep an eye on server loads, processing speed, and the functionality of various system components. This allows for the identification and quick resolution of issues, ensuring the system runs smoothly. Additionally, any bugs or glitches that weren’t discovered during testing should be addressed immediately.
Continuous Improvement and System Optimization
As employees begin to use the system on a day-to-day basis, opportunities for improvement often arise. This could include optimizing workflows, adding new features, or tweaking certain modules for efficiency. Regularly updating and fine-tuning the system based on feedback ensures it continues to add value long after the initial deployment.
User Feedback and Regular Updates
Gathering user feedback is a key part of the post-implementation process. Regular surveys, direct feedback sessions, or user forums can help capture issues users are facing, which can then be addressed in system updates. Keeping the system current and evolving helps improve user satisfaction and ensures the ERP system remains aligned with business needs.
Why FirstBit is the Right Choice for Your ERP Implementation
When selecting an ERP provider, it’s essential to
choose a partner that has the experience, industry knowledge, and support infrastructure to ensure a successful implementation. FirstBit stands out as an ideal choice for ERP implementation due to its deep understanding of the region’s business landscape and its tailored approach to solving industry-specific challenges.
Industry-Specific Expertise
FirstBit’s team brings decades of experience in ERP implementations, particularly in industries like construction, manufacturing, and retail. With this knowledge, FirstBit provides tailored ERP solutions that address the unique needs and complexities of these sectors. Their understanding of local tax, labor laws, and business practices ensures that businesses can achieve compliance while streamlining their processes.
Local Presence, Global Experience
Operating in Dubai since 2013, FirstBit combines international expertise with local insights. Their team understands the challenges faced by businesses in the GCC region and can offer solutions that cater to the specific needs of these markets.
Compliance and Accreditations
FirstBit’s ERP solutions are fully compliant with
UAE tax and labor laws. With their system accredited by the UAE Federal Tax Authority (FTA), businesses can rest assured that they won’t face legal or regulatory issues. This is a major benefit for companies looking to implement a tax-compliant ERP system in the region.
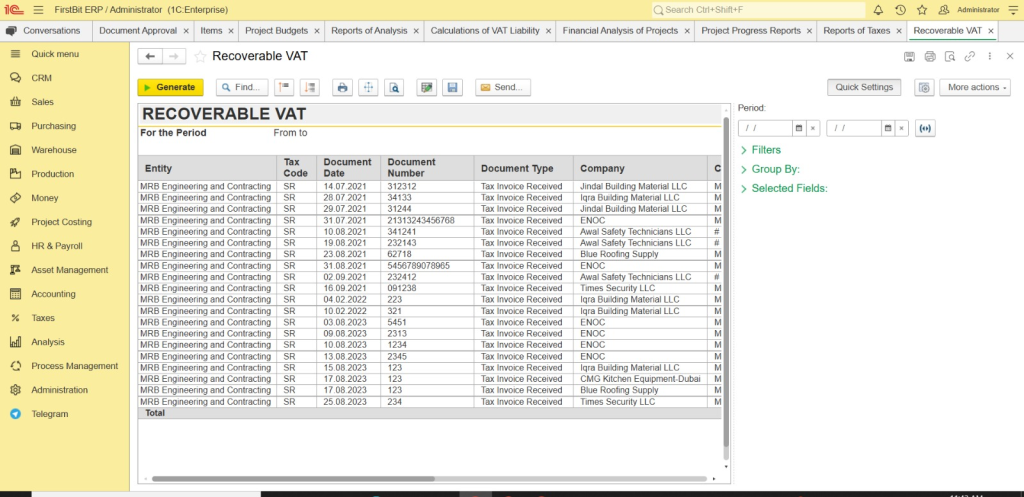
Recoverable VAT Report of FirstBit ERP Implementation
Responsive Customer Support
FirstBit’s commitment to providing responsive and reliable support ensures that businesses can quickly resolve any issues during the implementation and post-deployment phases. With a dedicated support team, FirstBit ensures that businesses continue to maximize their ERP system’s potential throughout its lifecycle.
Customer Support in FirstBit ERP
Free up your time with FirstBit ERP
Automate routine work and focus on growth
Request a demo
Conclusion
Implementing an ERP system is a transformative journey that can significantly enhance efficiency, decision-making, and business growth when executed correctly. By following the five crucial phases: planning, system design, testing, deployment, and post-implementation support, companies can avoid common pitfalls and maximize their ERP investment.
However, success doesn’t just depend on following steps; it requires the right partner. FirstBit’s industry expertise, local compliance knowledge, and dedicated support make it the ideal choice for businesses looking to implement ERP systems seamlessly. With a structured approach and the right guidance, your ERP implementation can drive long-term value, keeping your business agile and competitive in today’s fast-evolving market.
FAQ
1. What are the main objectives of the planning phase in an ERP implementation?
The planning phase defines business goals, identifies risks, sets realistic timelines/budgets, and assembles the right project team to ensure a smooth implementation.
2. How can businesses ensure smooth data migration during ERP implementation?
By cleaning and validating data beforehand, testing migration in stages, and scheduling the final transfer during low-activity periods to minimize disruptions.
3. What are the key challenges during the testing phase of ERP deployment?
Ensuring all modules function correctly, detecting integration issues early, and securing user feedback to fix usability gaps before go-live.
4. How can employee training impact the success of an ERP system?
Proper training boosts adoption, reduces errors, and ensures employees use the system effectively, maximizing ROI.
5. What steps should businesses take post-implementation to ensure continuous improvement?
Monitor performance, gather user feedback, provide ongoing support, and regularly update the system to align with evolving business needs.
Explore efficient ERP solutions for your construction business
Request a demo
Umme Aimon Shabbir
Editor at First Bit
Aimon brings a deep understanding of the modern construction business to her articles by providing practical content.